Why Linking Your PO System with ERP is a Game-Changer

Integrating a Purchase Order (PO) system with an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution is essential for food suppliers looking to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and financial control. A PO system streamlines procurement, ensuring seamless transactions with distributors, restaurants, and grocery stores, while an ERP integrates multiple business functions into a single platform. When combined, these systems eliminate redundancies, enhance data accuracy, and optimise procurement and financial management—critical factors in the fast-moving food supply industry.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of integrating a PO system with an ERP and how it can transform food supply operations.
The Role of a PO System in Procurement
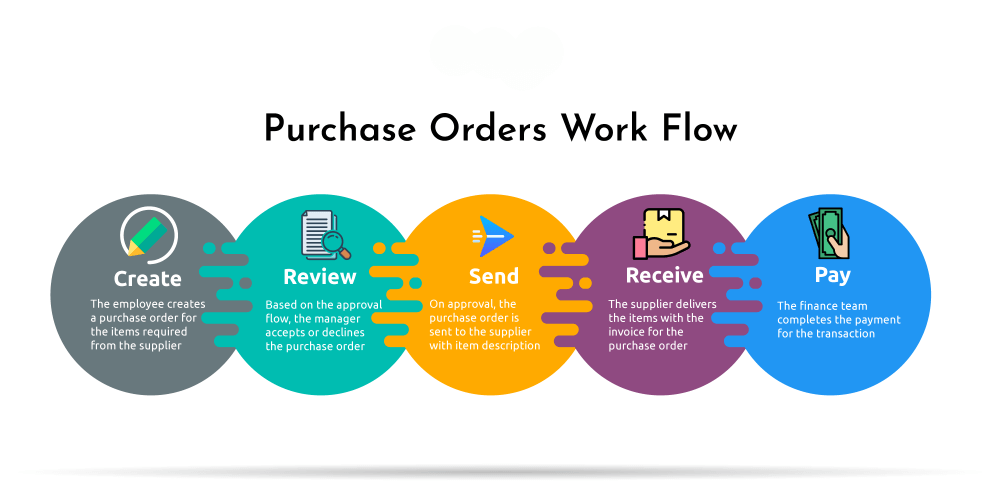
A PO system provides a structured approach to managing orders, ensuring timely deliveries, reducing errors, and improving supplier-buyer communication.
- Budget Control: Pre-approved purchases prevent overspending and keep procurement aligned with financial goals. Real-time expense tracking helps food suppliers manage cash flow and allocate resources effectively.
- Supplier & Distributor Management: Clear documentation fosters trust and accountability, reducing disputes and strengthening relationships with restaurants, retailers, and other buyers. Performance tracking allows food suppliers to assess partners based on order accuracy, delivery timeliness, and pricing consistency.
- Record Keeping & Compliance: Digital records simplify audits, financial reporting, and regulatory compliance. Automated data storage ensures accuracy, prevents fraud, and provides insights into purchasing trends—crucial for managing perishable goods and food safety standards.
Best Purchase Order Management Systems for Food Suppliers
The Core Functions of an ERP System
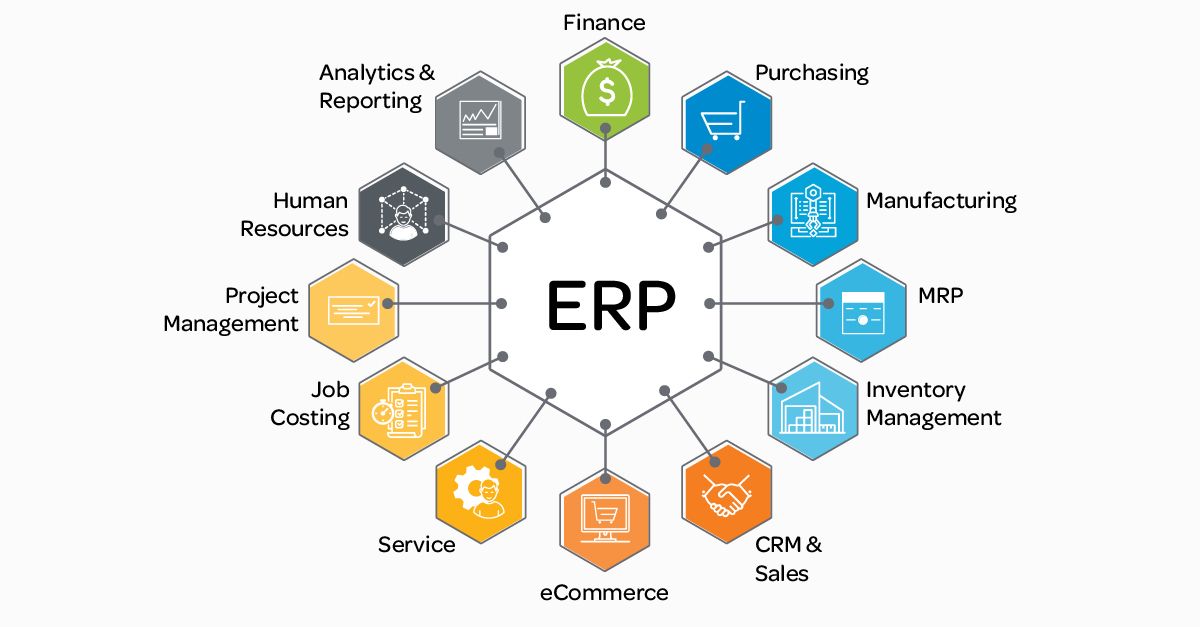
An ERP system centralises business processes, offering real-time access to data and improving decision-making across departments. Its key functions for food suppliers include:
- Financial Management: Tracks revenue, expenses, and budgets while ensuring regulatory compliance. Automated reporting and real-time financial insights help businesses manage cash flow, analyse profit margins, and reduce unnecessary costs.
- Supply Chain & Inventory Management: Enhances procurement, logistics, and inventory tracking, ensuring optimal stock levels, timely deliveries, and cost-efficient operations. Integrated data prevents overstocking or understocking of perishable goods.
- Order & Distribution Management: Manages order fulfillment, routing, and logistics, ensuring that fresh produce, dairy, or frozen foods reach customers on time. Route optimisation tools within an ERP system can help minimise delivery delays and fuel costs.
- Production & Quality Control: Supports manufacturing and processing workflows, ensuring adherence to food safety regulations, tracking expiration dates, and maintaining consistent product quality.
Best ERPs for Wholesale Suppliers
Why Integration Matters?

Linking a PO system with an ERP eliminates redundant tasks, improves data accuracy, and enables real-time synchronisation across procurement, inventory, and financial operations. This integration strengthens supply chain management, enhances compliance, and optimises overall efficiency.
1. Streamlined Procurement & Improved Data Accuracy
Manual order processing can lead to errors such as incorrect pricing, duplicate orders, or missed approvals. Integration minimises these risks by:
- Automating data transfer, reducing discrepancies and improving accuracy.
- Providing real-time inventory updates to prevent over-ordering or food waste.
- Standardising purchase workflows to ensure smooth, efficient operations.
2. Enhanced Cost Control & Budgeting
For food suppliers operating on tight margins, financial accuracy is essential. Integration provides:
- Real-time expenditure tracking to monitor costs and adjust budgets accordingly.
- Automated reconciliation of purchase orders, invoices, and payments to prevent financial errors.
- Advanced spend analysis to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimise supplier contracts.
3. Better Supplier & Customer Management
Managing vendor and customer relationships is key in food distribution. An integrated system helps by:
- Centralising supplier and customer data for improved tracking and performance assessment.
- Automating order approvals, reducing processing delays and minimising errors.
- Enhancing reporting capabilities, allowing suppliers to negotiate better pricing and assess distributor reliability.
4. Real-Time Inventory Visibility & Compliance
For food suppliers, managing inventory effectively while complying with food safety regulations is a challenge. Integration ensures:
- Instant access to inventory levels and expiration dates, reducing spoilage.
- Automated compliance tracking for food safety standards and traceability requirements.
- Proactive decision-making, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to supply chain disruptions.
5. Scalability & Business Growth
As food suppliers expand into new markets, handling growing procurement demands efficiently is critical. ERP integration supports scalability by:
- Reducing manual workload, allowing teams to focus on strategic growth.
- Supporting multi-location warehouses, distribution centers, and customers without adding complexity.
- Ensuring standardised processes, making business expansion more manageable and structured.
Why Food Suppliers Lose Money on Inventory & How to Fix It
Overcoming Integration Challenges

While integrating a PO system with an ERP offers significant advantages, food suppliers must address common challenges to ensure a seamless transition.
- Data Discrepancies: Mismatched formats or duplicate entries can disrupt workflows. Using data mapping tools and conducting thorough data cleansing ensures consistency and accuracy.
- User Resistance: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems due to unfamiliarity. Providing hands-on training, clear communication, and gradual onboarding can encourage smoother adoption.
- Overcomplicated Workflows: Adding unnecessary features or complex processes can hinder efficiency. Food suppliers should focus on essential workflows, ensuring integration remains streamlined and user-friendly.
- System Compatibility Issues: Integration can fail if APIs, middleware, or software versions are not aligned. Conducting compatibility tests and ensuring proper configuration prevents costly delays.
Software solutions like Open Pantry make PO and ERP integration even more seamless for food suppliers. Open Pantry offers real-time procurement tracking, automated vendor management, and enhanced financial reporting—helping businesses improve efficiency, reduce waste, and maintain compliance with food safety standards. By bridging the gap between purchase orders and ERP systems, Open Pantry empowers food suppliers to scale operations while optimising cost management.
For food suppliers, integrating a PO system with an ERP is a game-changer. By automating procurement, eliminating data silos, and providing real-time insights, businesses can optimize procurement, reduce waste, and make smarter financial decisions. Companies that leverage integrated systems gain a competitive edge in managing food supply chains, strengthening supplier relationships, and driving long-term growth. With solutions like Open Pantry, food suppliers can streamline operations and scale effectively in an increasingly competitive market.